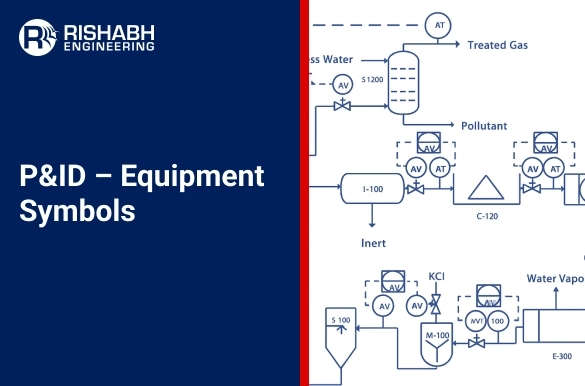
P&ID Equipment Symbols: Essential Components of System Design
The visual language of equipment symbols is essential for communicating the schematic elements of complicated systems when engineers and designers construct Process and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&ID). Standardized representations of different parts, such as pumps, valves, tanks, and heat exchangers, are provided by P&ID equipment symbols, making it simple for stakeholders to comprehend how materials and energy move through industrial systems. These symbols are essential to the precise design, construction, and operation of plants in process sectors like oil and gas, chemical, electricity, and food processing. Designing a system that is safe, effective, and compliant requires an understanding of P&ID symbols.
In this blog, we’ll explore the frequently used equipment P&ID symbols, while explaining their function, significance, and how they contribute to effective system design.

What Are P&ID Equipment Symbols?
Equipment P&ID symbols are a set of standardized graphic representations used in engineering drawings to depict physical devices or components in a process system. These symbols are governed by various international standards such as ISA-5.1 (International Society of Automation) or ANSI/ISA-5.1-2009, which ensures uniformity and clarity across industries.
The primary purpose of these symbols is to simplify the communication of design concepts between engineers, operators, and construction teams, while also ensuring that systems are built and maintained according to prescribed specifications.
Categories Of P&ID Symbols For Equipment
P&ID symbols can be broadly categorized into several groups based on the function or role of the equipment in the process. These include symbols for:
- Storage Equipment
- Heat Exchangers
- Pumps and Compressors
- Separators and Filters
- Mixers and Agitators
- Conveyors and Transport Equipment
Each group of symbols represents a particular set of operations, with their unique characteristics and purposes that drive the flow of materials, energy, and data within the system.
1. Storage Equipment Symbols:
Storage equipment is fundamental to every industrial process. These devices hold materials, liquids, gases, or chemicals at various stages of the production cycle. Some of the common storage equipment symbols include:
- Tank – General Basin: This symbol represents a general-purpose tank used for the storage of liquids. A tank basin is often used for holding raw materials, intermediate products, or waste streams.
- Tank – Floating Roof: Floating roof tanks are commonly used for storing volatile liquids such as petroleum or chemicals. The symbol depicts a tank with a roof that floats on the liquid, reducing evaporation and maintaining safety.
- Storage – Gas Cylinder: This symbol represents the storage of gases under high pressure, such as hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen. Gas cylinders are often used in industrial applications requiring pressurized gas supplies.
2. Heat Exchanger Symbols:
They are essential equipment used for transferring heat between two fluids without mixing them. Further, they play a crucial role in controlling temperatures within various industrial systems. The P&ID symbols for heat exchangers are diverse, as they represent different types based on design and heat transfer method.
- Heat Exchanger – Shell & Tube: It is one of the most used types. This symbol represents the equipment designed to transfer heat between two fluids through a series of tubes enclosed in a shell.
- Heat Exchanger – Plate Type: They feature multiple stacked plates to increase surface area and facilitate efficient heat exchange. The symbol for this equipment shows a series of plates arranged to maximize heat transfer.
- Heat Exchanger – Spiral: They are typically used for handling viscous fluids or fluids prone to fouling. Their design, featuring spirally wound tubes, is depicted by a unique P&ID symbol that differs from other heat exchanger types.
3. Pumps and Compressors:
They are considered as the vital components in fluid handling systems, designed to move or compress liquids and gases. Their symbols are among the most recognized in P&ID drawings.
- Pump: P&ID symbols for pumps represent equipment used to move liquids or slurries from one point to another. Pumps are classified by type—centrifugal, positive displacement, screw, diaphragm, and more—each serving a specific purpose depending on flow and pressure requirements.
- Compressor: They help increase the pressure of gases, making them essential for gas pipelines, HVAC systems, and process industries. The P&ID symbol for compressors typically resembles a mechanical unit with a symbol indicating flow direction.
- Blower: Like compressors but typically operate at lower pressures and higher volumes. They are often used for moving air or gas in industrial processes.
4. Separators and Filters:
Separators and filters are integral to maintaining the purity of liquids or gases within a system by removing unwanted particulates, oil, water, or solids.
- Separator: They help divide different phases into a mixture (e.g., liquid-liquid, liquid-gas, or gas-solid). They are represented by symbols indicating the type of separation (e.g., gravity, centrifugal) or the phase being separated.
- Filter – General: This symbol represents any general-purpose filtration device that removes particulates from liquids or gases. There are more specific filter symbols, including those for activated carbon filters, ion exchange filters, and rotary drum filters.
- Filter – Activated Carbon: Activated carbon filters are specifically used to remove contaminants from fluids, particularly gases. The P&ID symbol for this filter type typically includes a carbon bed or other filtration media to represent the carbon-based filtration process.
5. Mixers and Agitators:
Mixers and agitators are used to combine different materials, typically liquids or solids, in a process stream. The symbol for each piece of equipment can vary depending on the function it serves.
- Agitator: The agitator symbol represents a mechanical device that stirs or mixes materials within a container or vessel. Agitators are often used in reactors, tanks, and mixing vessels.
- Mixer: It represents equipment that combines substances, often using blades, paddles, or other moving parts, to achieve homogeneity in the process.
6. Conveyors and Transport Equipment:
In industrial systems, materials often need to be moved from one point to another. P&ID symbols for conveyors, transport vehicles, and elevators help illustrate how materials are moved through the system.
- Conveyor – Belt: The conveyor belt symbol represents a continuous loop of material used for transporting goods, raw materials, or products across a horizontal or inclined plane.
- Transport – Tank Car: It represents a rail car designed to transport liquids or gases in a tank container. It is widely used in industries such as chemicals, oil & gas, and food processing.
- Transport – Ship: This symbol is used to represent ships or vessels used for transporting bulk materials across water. It is especially relevant in industries where maritime transport plays a significant role, such as shipping and logistics.
P&ID – Pump Symbols
Equipment P&ID symbols represent a wide range of industrial devices, each intended to carry out certain functions inside a process system. For instance – conveying system design and operating flows, these symbols are crucial for anything from pumps and compressors to tanks, heat exchangers, and filters. And, given that they stand for equipment that usually depict vital processes including material transportation, energy transmission, separation, and storage. Further, it is imperative to comprehend the meaning behind each symbol. Ensuring the safe and effective design, building, and operation of industrial systems depends critically on the proper use and interpretation of these symbols.
Let’s explore the detailed representation of equipment within P&IDs that we consider;
Tank – General Basin: Used for general liquid storage purposes.

Tank – Floating Roof: Storage tank with floating roof system.

Vessel – General Column: Vertical vessel for separation or distillation.

Vessel – General: Container for holding fluids or gases.

Vessel – Conical Head: Vessel with tapered conical bottom shape.

Vessel – Dished Head: Vessel with a curved, dished top.

Vessel – Trays: Vessel with trays for separation processes.

Vessel – Spherical: Spherical vessel for holding liquids or gases.

Vessel – Fixed Bed: Vessel with a fixed bed of material.

Vessel – Fluidized Bed: Vessel with material in a fluidized state.

Vessel – Full-Tube Coil: Vessel with coils for heat exchange.

Vessel – Semi-Tube Coil: Vessel with partial coils for heat exchange.

Vessel – Jacketed: Vessel with an external jacket for heating/cooling.

Storage – Container: Generic container for storing materials or liquids.

Storage – Bag: Storage equipment for bagged material.

Storage – Barrel Drum: Cylindrical container for bulk material storage.

Storage – Gas Cylinder: High-pressure container for storing gases.

Furnace – Industrial: High-temperature device for industrial heating processes.

Pump: Mechanical device for moving liquids or gases.

Compressor: Device for compressing gases or air.

Blower: Equipment for moving air or gas.

Heat Exchanger – General 1: General-purpose equipment for heat transfer.

Heat Exchanger – General 2: Another general heat exchanger configuration.

Heat Exchanger – General Cooling Tower: Heat exchanger for cooling water or air.

Heat Exchanger – Spiral: Heat exchanger with spiral coil design.

Heat Exchanger – Double Pipe: Heat exchanger using two concentric pipes.

Heat Exchanger – Plate Type: Heat exchanger using multiple stacked plates.

Heat Exchanger – Finned- Tube: Heat exchanger with fins to increase surface area.

Heat Exchanger – Tube Bundle (U-Tube): U-tube heat exchanger for heat exchange processes.

Heat Exchanger – Shell & Tube Bundle (U-Tube): Shell and U-tube bundle heat exchanger.

Heat Exchanger – Tube Bundle (Floating Head): Tube bundle with a floating head for heat exchange.

Heat Exchanger – Floating Head Tube Bundle: Tube bundle design with floating head connection.

Heat Exchanger – Shell & Tube: Common heat exchanger with shell and tubes.

Heat Exchanger – Spray Cooler: Heat exchanger with spray cooling design.

Heat Exchanger – Steam Boiler: Heat exchanger used for steam generation.

Heat Exchanger – Film Evaporator: Heat exchanger for evaporating liquids with film.

Heat Exchanger – Tube Coil: Heat exchanger with coil tubes for heat exchange.

Heat Exchanger – Heating/Cooling: Equipment designed for heating and cooling fluids.

Heat Exchanger – Burner Firing System: ASystem for heating using burner firing.

Driver: Machine providing mechanical power to other equipment.

Agitator: Equipment used to mix or stir materials.

Mixer: Device for combining substances or materials.

Filter – General: Equipment for filtering particles from fluids.

Filter – Liquid: Filter used specifically for liquid filtration.

Filter – Suction: Filter used in suction line applications.

Filter – Activated Carbon: Filter that uses activated carbon for filtration.

Filter – Belt for Gases: Belt filter for separating gases.

Filter – Ion Exchange: Filter utilizing ion exchange for purification.

Filter – Rotary Drum: Rotating drum filter for continuous filtration.

Filter – Fixed Bed: Fixed bed filter using media for filtration.

Filter – Press: Pressure-driven filter for separating solid/liquid phases.

Filter – Fixed Bed: Fixed bed filter using media for filtration.

Filter – HEPA: High-efficiency particulate air filter for particles.

Filter – Gases Packed Bed: Gas filtration using a packed bed of material.

Separator: Equipment for separating different phases of materials.

Centrifuge – General: Equipment for separating materials using centrifugal force.

Centrifuge – Perforated Shell: Centrifuge with perforated shell for material separation.

Centrifuge – Pusher: Centrifuge using pusher mechanism for solids separation.

Centrifuge – Screw: Centrifuge with screw for continuous separation.

Centrifuge – Screw Perforated Shell: Centrifuge with screw and perforated shell.

Centrifuge – Solid Shell: Centrifuge with solid shell for high-efficiency separation.

Centrifuge – Disk: Centrifuge utilizing disks for material separation.

Screening Device: Equipment used for separating materials by size.

Softer – General: Device for softening hard water or materials.

Sorting – General: Equipment for sorting materials based on properties.

Dryer – General: Equipment used to remove moisture from materials.

Dryer – Disk: Disk-type dryer for material dehydration.

Dryer – Fluidized Bed: Dryer using fluidized bed for moisture removal.

Dryer – Oven: Heat-based dryer for material dehydration.

Dryer – Roller Conveyor Belt: Dryer with rolling conveyor belt for drying.

Dryer – Rotary Drum: Drum-type dryer used for continuous drying.

Dryer – Spray: Spray drying technique for rapid moisture removal.

Crusher: Equipment used for crushing materials into smaller sizes.

Mill: Machine for grinding materials into fine powder.

Crusher: Equipment used for crushing materials into smaller sizes.

Mill: Machine for grinding materials into fine powder.

Elevator – Bucket: Bucket elevator used for vertical material transport.

Conveyor – General: Equipment for moving materials horizontally or vertically.

Conveyor – Belt: Belt conveyor for continuous material transport.

Conveyor – Chain: Chain conveyor for transporting heavy materials.

Conveyor – Screw: Screw conveyor for materials handling.

Conveyor – Vibrating: Vibrating conveyor for smooth material flow.

Transport – Ship: Ship used for transporting bulk materials.

Transport – Tank Car: Tank car for transporting liquids or gases.

Transport – Box Truck: Box truck used for transporting goods.

Transport – Industrial Truck: Industrial truck used for material handling.

Shaping Machine: Pelletizing Disk: Equipment for forming materials into pellets.

Shaping Machine – Piston Press: Machine for pressing materials using pistons.

Shaping Machine – Roller Press: Press using rollers for material shaping.

Shaping Machine – Screw Type Extruder: Extruder that uses screws for shaping materials

Shaping Machine – General Coarsening: Equipment used for coarse shaping of materials.

Shaping Machine – Extruder: Equipment used for shaping materials into profiles.

Solids Proportioner – General: Equipment for proportioning solid materials accurately.

Distribution Device – Rotary Table: Rotary table for material distribution and transfer.

Feeder – Rotary Valve: Rotary valve used for controlling material flow.

Scale – Belt: Belt scale for measuring materials during transport

Scale – General: General weighing scale for materials or equipment.

Scale – Weighing Platform Floor: Platform scale for bulk material weighing.

Misc – Bulk Storage: Generic storage unit for bulk materials.

Misc – Stack Chimney: Stack or chimney for exhaust or venting

Misc – Gas Flare: Equipment for safely burning off excess gas.

Misc – General Electrolysis Cell: Cell used for electrolysis reactions.

Misc – General Hood: Ventilation hood for air or gas extraction.

The Importance of Standardization in P&ID Symbols for Equipment
One of the most important aspects of P&ID equipment symbols is their standardization. The use of standardized symbols across industries and projects ensures that engineers and technicians worldwide can interpret P&ID diagrams correctly, regardless of location or company. This uniformity also helps prevent misinterpretations that could result in system failures or safety issues.
For example, a pump symbol looks the same on a P&ID diagram, whether the project is in the United States, Europe, or Asia. This universality is critical in industries with a global presence, such as oil & gas, where safety, efficiency, and compliance are paramount.
Best Practices for Reading P&ID Equipment Symbols
While P&ID diagrams provide a detailed and systematic representation of an industrial system, reading them efficiently requires some practice. Here are a few tips to help you interpret these symbols:
- Familiarize Yourself with the Legend: Each P&ID drawing should have a legend or key that explains the symbols and their meanings. Make sure you are familiar with the legend before diving into the diagram.
- Understand Flow Direction: Arrows on P&ID symbols typically indicate the flow of materials or energy. Pay attention to the direction of the arrows to understand how fluids or gases will move through the system.
- Look for Additional Information: Symbols on P&ID diagrams may include tags or numbers that identify the specific equipment and its function. This information can help you better understand the system’s design.
- Pay Attention to Line Types: Different types of lines (solid, dashed, or dotted) on a P&ID diagram represent various aspects of the system, such as piping, electrical connections, or instrument loops. Understanding these lines is crucial to interpreting the diagram.
Final Words
To sum up, P&ID equipment symbols are essential for anybody involved in the planning, execution, and upkeep of industrial systems. These standardized symbols provide accuracy, safety, and compliance by assisting engineers in communicating intricate process information in an understandable manner. It is essential to comprehend P&ID symbols whether constructing a new plant, troubleshooting current systems, or examining technical documentation. Effective communication will become increasingly important in process design as industries continue to change. Gaining proficiency with P&ID equipment symbols will increase your ability to support the success of industrial systems in a variety of industries and reinforce the importance that equipment engineering services play in ensuring safe, effective, and compliant operations.
Need Assistance With P&ID Equipment Symbols?
Our specialists can help you accurately design and implement the right symbols for your systems, ensuring compliance and clarity.
Related Blogs
Related Blogs
Best Structural Engineering Software for Accurate Analysis
Finding tools that simplify and improve the accuracy of the…
Detailed Engineering Considerations for Project Success
Engineering projects today require meticulous planning and execution across various…